Hey, I'm Steve
a
Cybersecurity Expert.
CompSci Professor.
Content Creator.
My skills and knowledge in the latest techniques and technologies have helped me excel in investigations of cyber crimes, and I bring this expertise to my consulting clients. Along with my consulting work, I also enjoy using my knowledge and skills to create engaging and informative content on Youtube and Udemy. As a computer science professor, I take pride in sharing my expertise with the next generation of InfoSec professionals.

My Current Courses

Are you looking to jumpstart your career in the IT industry? Look no further than the CompTIA A+ certification training by Steve Nicholson and Mike Meyers.
This comprehensive course is designed to provide you with the knowledge and skills you need to pass the CompTIA A+ certification exam and start your journey towards a successful career in IT.
Steve Nicholson and Mike Meyers are experts in the field with decades of experience in the industry and have created this video series to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date curriculum that covers the latest technologies and best practices that you will need to know in order to become CompTIA A+ certified.
With our training, you will gain a solid understanding of key concepts such as hardware and software troubleshooting, security, and operating systems. The course is divided into easy to follow modules that are designed to build on each other, ensuring that you have a solid foundation before moving on to more advanced topics.
Our training program includes:
- Access to over 30 hours of HD video training with state of the art equipment
- Downloadable study materials and resources
- Interactive quizzes and exercises to test your knowledge and skills
- 24/7 access to our online learning platform
By taking this training, you’ll be preparing yourself for the CompTIA A+ certification exam, which is globally recognized and highly valued by employers. This certification proves that you have the knowledge and skills necessary to be successful in the IT industry.
Don’t wait any longer. Start your journey to a successful IT career today. Enroll in the CompTIA A+ certification training by Steve Nicholson and Mike Meyers and get on the fast track to becoming a certified PC technician.
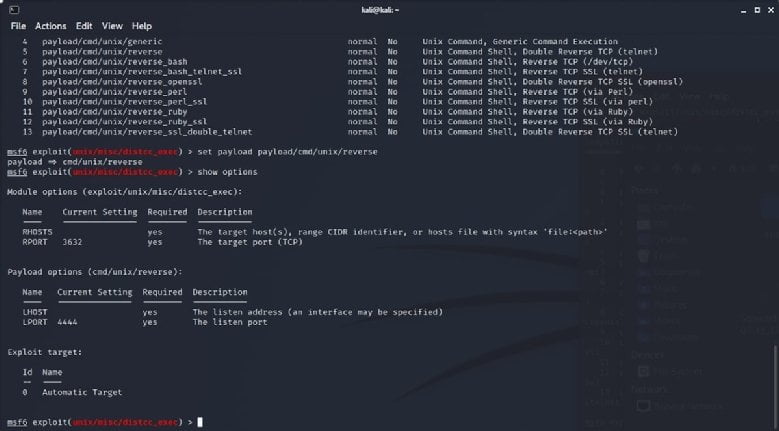
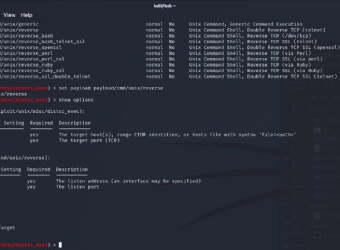
CIS4200: Penetration Testing with Kali
Students in my Penetration Testing course, CIS4200, are constantly tasked with reverse engineering, replicating, or defending against modern security vulnerabilities. At the beginning of each module they are assigned a lab-based walkthrough that introduces new concepts, reinforces old concepts, and eliminates homework boredom. Then they are slowly guided deeper into each tool and skillset before finally being asked to demo what they have learned and capture a hidden flag. This type of incremental reinforced learning is widely prevalent in our sector, and the Capture the Flag (CTF) scenarios my students face are on par with those the top training agencies utilize and are all based on real world vulnerabilities and attacks.
This course is currently offered both as a for-credit college course and as a private instructor-led teaching.
ISM4324: Computer Forensic Analysis
This course focuses on the techniques and methods used to conduct forensic examinations of digital evidence. The course covers the entire process of computer forensics, from the initial seizure and preservation of evidence, to the analysis and presentation of findings in a court of law.
One of the main topics covered in the course is the use of forensic tools and software, such as EnCase and FTK, to recover and analyze data from various types of digital devices, including computers, smartphones, and storage media. Students will also learn about the legal and ethical considerations involved in computer forensics and the proper handling of evidence to ensure its admissibility in court.
The course also covers the various types of digital evidence that may be encountered in a forensic examination, including deleted files, hidden data, and encrypted files. Students will learn how to identify and extract relevant evidence and how to present their findings in a clear and concise manner.
In addition to the technical aspects of computer forensics, the course also covers the broader context of cybercrime and its impact on society. Students will learn about the different types of cybercrime, such as hacking, identity theft, and cyberstalking, and the legal and investigative challenges they pose.
This course is currently offered only as a for-credit college course.
ISM4320: Applications in Information Security
explores the practical applications of information security in different industries and organizations. The course covers a wide range of topics, including risk management, threat intelligence, incident response, and compliance.
One of the main focuses of the course is on the development of information security policies and procedures. Students will learn how to identify and assess security risks, and how to develop and implement effective security measures to mitigate those risks. The course also covers incident response planning and incident management, providing students with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively to security incidents.
Another important aspect of the course is the exploration of different types of cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Students will learn about the latest threats, including advanced persistent threats (APTs), and how to identify, assess, and defend against them. The course also covers compliance and regulatory requirements, providing students with an understanding of the legal and regulatory framework surrounding information security.
The course also provides hands-on experience through the use of various security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability scanners. Students will have the opportunity to apply the concepts and techniques learned in class to real-world scenarios through lab exercises and projects.
My WeBlog
CompTIA A+: All 20 Linux commands in less than 20 minutes
During tonight’s Total Seminars Discord Study Hall, I covered all 20 Linux CLI commands you need to know in order
CompTIA A+: All 20 Linux commands in less than 20 minutes
During tonight’s Total Seminars Discord Study Hall, I covered all 20 Linux CLI commands you need to know in order to pass the CompTIA A+ exam.
Breaking Down the Cyber Kill Chain: Understanding and Defending Against Cyber Attacks
In the field of cybersecurity, one of the most widely-used frameworks for describing the stages of a cyber attack is
Breaking Down the Cyber Kill Chain: Understanding and Defending Against Cyber Attacks
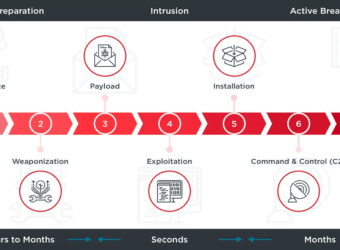
In the field of cybersecurity, one of the most widely-used frameworks for describing the stages of a cyber attack is the Cyber Kill Chain. Developed by Lockheed Martin, this framework is a useful tool for understanding the various stages of an attack and the steps that organizations can take to defend against them.
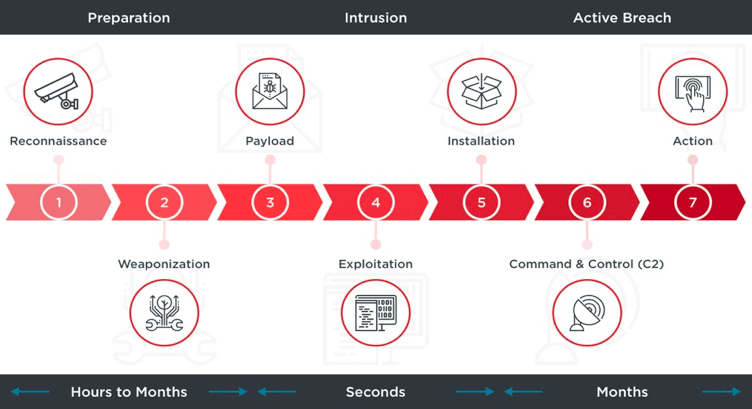
At a high level, the Cyber Kill Chain consists of seven stages:
- Reconnaissance: The attacker gathers information about the target and identifies potential vulnerabilities.
- Weaponization: The attacker creates a weapon (e.g., a malicious file or exploit) that can be used to exploit the identified vulnerabilities.
- Delivery: The attacker delivers the weapon to the target (e.g., via email or a compromised website).
- Exploitation: The attacker uses the weapon to exploit the identified vulnerability and gain access to the target’s systems.
- Installation: The attacker installs a persistent presence on the target’s systems to maintain access and control.
- Command and control: The attacker establishes a command and control infrastructure to remotely manage the compromised systems.
- Actions on objectives: The attacker achieves their intended goal, which could be data theft, destruction of data or systems, or some other malicious action.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these stages and how they can be defended against.
- Reconnaissance: In this stage, the attacker is gathering information about the target to identify potential vulnerabilities. This could involve scanning the target’s networks, searching for public-facing vulnerabilities, or even social engineering to gather information about the target’s employees. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as network segmentation, restricting access to sensitive information, and conducting regular security awareness training for employees.
- Weaponization: In this stage, the attacker creates a weapon that can be used to exploit the identified vulnerabilities. This could involve creating a malicious file, exploiting a software vulnerability, or even using social engineering to trick the target into executing the weapon. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as patching software vulnerabilities, deploying antivirus and antimalware solutions, and using email filtering to block malicious attachments.
- Delivery: In this stage, the attacker delivers the weapon to the target. This could involve sending a malicious email, compromising a website, or even using physical media (such as a USB drive) to deliver the weapon. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as email filtering, web application firewalls, and limiting the use of external media on corporate systems.
- Exploitation: In this stage, the attacker uses the weapon to exploit the identified vulnerability and gain access to the target’s systems. This could involve running code on the target’s system, bypassing authentication controls, or even using a privilege escalation exploit to gain administrative access. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as network segmentation, implementing strong authentication controls, and deploying intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Installation: In this stage, the attacker installs a persistent presence on the target’s systems to maintain access and control. This could involve installing a backdoor, creating a new user account, or even modifying system files to ensure that the attacker can maintain access. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as deploying host-based intrusion detection and prevention systems, regularly monitoring system logs, and limiting the use of administrator accounts.
- Command and control: In this stage, the attacker establishes a command and control infrastructure to remotely manage the compromised systems. This could involve setting up a remote access tool, using a compromised server as a proxy, or even using social media platforms to communicate with the compromised systems. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as blocking outgoing traffic to known command and control servers, using intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regularly monitoring network traffic.
- Actions on objectives: In this final stage, the attacker achieves their intended goal, which could be data theft, destruction of data or systems, or some other malicious action. This could involve stealing sensitive data, encrypting critical systems, or using compromised systems to launch further attacks against other targets. To defend against this stage, organizations can implement measures such as deploying data loss prevention solutions, implementing strong access controls, and regularly conducting vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.In conclusion, the Cyber Kill Chain is a useful framework for understanding the various stages of a cyber attack and the steps that organizations can take to defend against them. By implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity program that addresses each stage of the Cyber Kill Chain, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of a successful cyber attack. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution to cybersecurity, understanding the Cyber Kill Chain and implementing appropriate defenses can go a long way toward protecting organizations from the ever-evolving threat of cyber attacks.
Python Tool: Quick Metadata, Stego, and Reverse GIS
A lightweight Python tool that accomplishes 3 objectives for the DFIR professional (scroll down for a more advanced explanation of

Python Tool: Quick Metadata, Stego, and Reverse GIS
A lightweight Python tool that accomplishes 3 objectives for the DFIR professional (scroll down for a more advanced explanation of each function):
- Extracts metadata from media files, and prints out any metadata that’s found
- Checks for steganography in both images and video frames
- Performs a reverse GIS on images
import exifread
from stegano import lsb
from google_images_search
import GoogleImagesSearch
import cv2
# initialize the GoogleImagesSearch object with your API key and project CX
gis = GoogleImagesSearch('your_api_key', 'your_project_cx')
def get_metadata(filepath):
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
# read the metadata from the file
tags = exifread.process_file(f)
# print out any hidden metadata found
for tag in tags:
if tag.startswith("Image") or tag.startswith("EXIF"):
print(f"{tag}: {tags[tag]}")
# check for steganography in image files
if filepath.endswith(".jpg") or filepath.endswith(".png"):
secret = lsb.reveal(filepath)
if secret:
print(f"Steganography detected: {secret}")
# perform reverse image search on image files
gis.search_image(filepath)
for image in gis.results():
print(f"Matching image found: {image.url}")
# check for steganography in video frames
if filepath.endswith(".mp4") or filepath.endswith(".avi"):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(filepath)
frame_count = 0
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
frame_count += 1
cv2.imwrite(f"temp_frame_{frame_count}.jpg", frame)
get_metadata(f"temp_frame_{frame_count}.jpg")
cap.release()
# example usage
get_metadata("example.jpg")
get_metadata("example.mp4")
Here’s a breakdown of how the script works:
- We begin by importing the necessary libraries:
exifreadis used to extract metadata from media files.steganois used to detect hidden messages in image files.google_images_searchis used to perform reverse image searches on image files.cv2is used to extract frames from video files.
- Next, we create an instance of
GoogleImagesSearchand pass in our API key and project cx. This will allow us to search for similar images on Google. - The
get_metadata()function takes a file path as input and checks if the file is an image or video file. - If the file is an image file, we first use
exifreadto extract any metadata that may be hidden in the file. We loop through all the tags in the metadata and print out any that start with “Image” or “EXIF”. - Next, we use
steganoto check if there are any hidden messages in the image file. If a hidden message is found, we print it out. - We then use
google_images_searchto perform a reverse image search on the image file. We callgis.search_image(filepath)to search for similar images on Google, and loop through the results withgis.results(). For each result, we print out the URL of the matching image. - If the file is a video file, we use
cv2to extract frames from the video file. We loop through all the frames and save them as temporary image files. We then callget_metadata()on each temporary image file to perform the same metadata and steganography detection as we did for image files. - Finally, we call
get_metadata()on the input file to run the entire script.
Note that this script can potentially violate privacy and security, so make sure you have proper authorization and use the script responsibly. Also, extracting frames from video files can be time-consuming and memory-intensive, so it may not be practical for very long videos or for systems with limited hardware resources.
“The Dark Side of AI: How Chatbots like ChatGPT Threaten Information Security”
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has brought about many exciting advancements in technology, but it also poses a significant
“The Dark Side of AI: How Chatbots like ChatGPT Threaten Information Security”
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has brought about many exciting advancements in technology, but it also poses a significant threat to the information security industry. One example of this is the use of AI-powered chatbots like ChatGPT.
ChatGPT, as well as other similar chatbots, can mimic human communication so well that it can be difficult to distinguish between a human and a machine. This poses a major problem for organizations that rely on human verification to authenticate users and prevent fraud. Cybercriminals can use chatbots to bypass these security measures and gain access to sensitive information.
Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots can also be used to launch sophisticated phishing attacks. Cybercriminals can train chatbots to impersonate trusted individuals or organizations and trick victims into providing sensitive information. These attacks can be difficult to detect, as they often involve a level of human-like conversation that traditional anti-phishing measures may not be able to detect.
Another concern is the use of AI in Automated Social Engineering, where attackers use AI to craft highly personalized phishing or scamming messages to specific individuals based on their behaviours, demographics and other information that is publicly available, making it much harder for the individual to detect the scam.
In addition to these concerns, AI-powered chatbots can also be used for spreading misinformation and propaganda. The ability of chatbots to generate large amounts of content and impersonate multiple identities makes them an attractive tool for spreading disinformation and sowing discord online.
It’s important for organizations to stay vigilant and take appropriate measures to protect themselves from these threats. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication, educating employees on how to spot and avoid phishing attacks, and staying up-to-date on the latest threat intelligence. Additionally, organizations should also consider using AI-based security solutions that can detect and block AI-powered attacks.
In conclusion, while AI-powered chatbots like ChatGPT have the potential to bring many benefits to the industry, they also pose a serious threat to information security. It’s crucial that organizations take steps to protect themselves from these threats and stay vigilant in the face of an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Determining the end of a Product’s Life Cycle: a Universal problem
This post was inspired by our recent trip to Universal Studios Orlando. After 5 ride breakdowns, including 3 that happened

Determining the end of a Product’s Life Cycle: a Universal problem
This post was inspired by our recent trip to Universal Studios Orlando. After 5 ride breakdowns, including 3 that happened while we were in the middle of the ride, I felt the need to redefine the standard PLC for clarity.
The product life cycle of technology refers to the stages that a technology product goes through from its development to its eventual retirement or obsolescence. Understanding the product life cycle can be important for businesses that rely on technology, as it can help them plan for the future and make informed decisions about investment and resource allocation.
At Universal Studios Florida, ride breakdowns can be a common occurrence due to the high demand and use of the rides. In order to minimize the impact of these breakdowns, it is important for the park to understand the product life cycle of the technology used in its rides and to plan accordingly.
The first stage of the product life cycle is the development stage, during which a new technology product is designed and developed. At this stage, a company may invest heavily in research and development in order to create a new product that meets the needs of its customers.
The next stage is the introduction stage, in which the product is launched and made available to the public. At this stage, a company may experience high costs due to marketing and promotion efforts, as well as the need to train staff and build infrastructure to support the new product.
The growth stage is the next stage of the product life cycle, during which demand for the product begins to increase. This can be a lucrative time for a company, as it may begin to see increased profits due to the growing demand for its product.
The maturity stage is the stage in which the product becomes well-established and demand begins to level off. At this stage, a company may focus on cost-cutting measures in order to maintain profitability.
Finally, the decline stage is the final stage of the product life cycle, during which demand for the product begins to decline and the product becomes obsolete. At this stage, a company may choose to retire the product or to continue supporting it with minimal investment.
In the case of ride breakdowns at Universal Studios Florida, it is important for the park to understand the product life cycle of the technology used in its rides. This can help the park plan for the future and make informed decisions about when to invest in new technology or retire older technology. By understanding the product life cycle, the park can minimize the impact of ride breakdowns and ensure that its guests have a positive experience.
Securing the Vote: A Look at the Digital Election Security Measures Needed for the Upcoming POTUS Election
The integrity of our electoral process relies on the ability to trust that every vote is counted accurately, and that

Securing the Vote: A Look at the Digital Election Security Measures Needed for the Upcoming POTUS Election
With the upcoming presidential election, it’s crucial that we ensure the security of our digital voting systems. The integrity of our electoral process relies on the ability to trust that every vote is counted accurately, and that the outcome of the election reflects the will of the people. However, with the increased use of technology in the voting process, there are also increased opportunities for malicious actors to interfere.
One of the main concerns regarding digital election security is the potential for hackers to tamper with voting machines or voting systems. This can include manipulating vote tallies, disrupting the voting process, or even preventing eligible voters from casting their ballots. To combat this, it’s crucial that voting systems are secured with robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication. Additionally, voting systems should be regularly audited and tested for vulnerabilities, and any identified issues should be promptly addressed.
Another concern is the use of social media and other online platforms to spread disinformation or manipulate public opinion. This can include creating fake news stories, impersonating official sources, or even using AI-powered chatbots to impersonate real people and influence the opinions of potential voters. To counter this, it is important that we have robust fact-checking mechanisms in place, and that both the public and media are educated on how to identify and combat disinformation. Additionally, social media platforms have a responsibility to monitor and remove disinformation, and work closely with election officials.
The use of online voting systems also poses significant security risks. Online voting systems are vulnerable to hacking, malware and phishing attacks. There is also a potential for vote-buying, voter coercion, and voter impersonation. To ensure the security and integrity of online voting systems, it’s important to ensure that these systems are built with robust security measures such as end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication. Additionally, it’s crucial that these systems are regularly audited and tested for vulnerabilities, and that any identified issues are promptly addressed.
It’s also important to make sure that the voter registration process is secure, to prevent voter fraud and manipulation. This can include using multi-factor authentication to verify voter identities, and ensuring that voter registration databases are kept up to date and protected against hacking attempts.
In conclusion, ensuring the security of our digital voting systems is crucial for the integrity of our electoral process. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, regularly auditing and testing for vulnerabilities, and educating the public and media on how to identify and combat disinformation, we can help ensure that the outcome of the upcoming presidential election reflects the will of the people. Additionally, it’s important to make sure that the voter registration process is secure, to prevent voter fraud and manipulation.